What Are The Major Differences Between Nervous Systems In Animal Phyla?
What Are Deuterostomes And Protostomes?
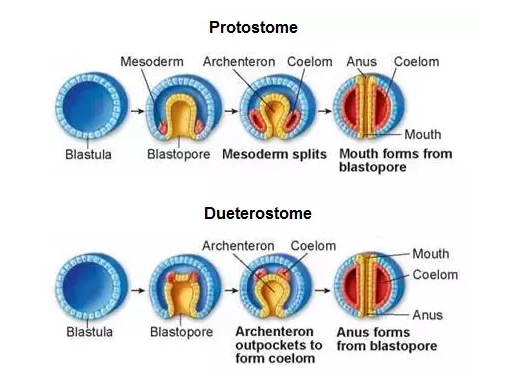
Deuterostomes are the animals whose embryonic development undergoes radial cleavage. In other words, the jail cell division planes accept place radially during the formation of the blastula through cleavage of the fertilized egg embryo. In deuterostomes, the first cavity formed by the blastopore ends upwards as the organism'south anus, while the mouth is formed secondarily on the opposite side. The deuterostomes can be grouped taxonomically into the following clades:
- Echinodermata e.g starfish, sea urchin, crinoids, body of water cucumber, blastoid, cystoidea, Eocrinoidea etc.
- Chordates include marine and terrestrial animals (mammals, reptiles, amphibians, frog, turtle, lizard, bat, tetrapods, Sloth, and jawless fish).
- Cephalochordata e.g lancelets
- Urochordata which includes tunicates (sea squirts), Ascidians, Larvacea, Thaliacea etc.
- Vertebrata
- Hemichordata e.g planctosphaeroidea, graptolithina, pterobranchia, acorn worm
Protostomes is any fellow member of the lower invertebrate phyla in which the mouth appears before the anus during development, cleavage is spiral and determinate and the coelom forms every bit a splitting of the mesoderm.Examples of protostomes include:
- Leeches
- Insects (beetles, ants, flies, crickets, butterflies, flees, cicada, bees)
- Spiders
- Crustaceans (venereal, lobsters, crayfish, woodlice, bernacles)
- Velvet worms
- Centipedes and millipedes
- Earthworms
- Squid
- Octopus
- Snail and slugs
- Bivalve mollusks (clams, oysters, mussels, scallops)
The master deviation between protostomes and deuterostomes is at the point of the blastopore. In protostomes, the blastopore develops into the oral cavity and the opposite cavity develops into the anus. In deuterostomes (the group that includes vertebrates and echinoderms), the blastopore develops into anus. Below, get to understand more differences between deuterostomes and protostomes.
Likewise Read: Divergence Between Phytoplanktons and Zooplanktons
Characteristics Of Protostomes
- The blastopore in a protostome develops into a mouth.
- Protostomes are referred to as schizocoelomates because the coelom is developed by splitting of the solid mass of the embryonic mesoderm.
- In protostomes, the gut is tunneled into embryo and forms anus.
- There is no archenteron evolution in protostomes. Archenteron is a rudimentary alimentary cavity formed during the early stages of embryo development. Information technology usually develops into mosederm and endoderm of a living organism.
- Protostomes can be priapulids.
- The nervous system of protostomes is solid, ventral nerve cord. Information technology is also important to annotation that many deuterostomes also have pharyngeal gill slits.
- Protostomes are less evolved and complex in their torso compositions than Deuterostomes.
- Protostomes are multi-ciliated cells.
- All the remaining bilaterian phyla are grouped into protostomes or divided into ii groups: protostomes and lophophorate.
- Protostomes contains less phyla and species than Deuterostomes.
- In protostomes, the anus arises secondarily.
- Protostomes exhibit determinate cleavage. Determinate cleavage is whereby the blastomere produced in the early stages of embryo development do not have capacity to develop into independent embryos.
- Protostomes undergo spiral cleavage. In spiral cleavage, the blastomeres of the animal pole are rotated with respect to those of the vegetal poles.
- Protostomes include flat worms, annelids, arthropods, mollusks and other less complex organisms.
Characteristics Of Deuterostomes
- The blastopore in deuterostomes develops into an anal opening.
- Deuterostomes are referred to as enterocoelous because the longitudinal pouches of the archenteron forms the coelom.
- In deuterostomes , the rima oris is formed by gut existence tunneled into embryo.
- Deuterostomes have archenteron development in the early stages of embryo germination.
- Deuterostomes are always enterocoelous.
- The nervous system of deuterostomes is equanimous of hollow nerve string.
- Deuterostomes are more evolved and complex in their body compositions than protostomes.
- Deuterostomes are all mono-cliated.
- Deuterostomes mainly includes echinoderms, hemichordes and chordates
- Deuterostomes contains less phyla and species than protostomes.
- In deuterostomes, the mouth arises secondarily.
- Deuterostomes exhibit indeterminate cleavage. Indeterminate cleavage is whereby all early blastomeres accept the capacity to develop into a consummate embryo.
- Deuterostomes undergo radial cleavage. In radial cleavage, the blastomeres of upper tiers are positions directly above those of lower tiers. This somewhen results in radial symmetry across beast pole and vegetal pole.
- Deuterostomes include chordates, echinoderms, pogonophora, hemichordates and other higher and circuitous organisms. Deuterostomes includes higher animals like human beings, monkeys, birds etc.
Also Read: Divergence Between Amphibian And Reptile
Protostomes Vs. Deuterostomes In Tabular Form
| BASIS OF COMPARISON | DEUTEROSTOMES | PROTOSTOMES |
| Blastopore | Blastopore in deuterostomes develops into an anal opening. | The blastopore in a protostome develops into a mouth. |
| Coelom | They are referred to every bit enterocoelous considering the longitudinal pouches of the archenteron forms the coelom. | They are referred to as schizocoelomates because the coelom is developed by splitting of the solid mass of the embryonic mesoderm. |
| Oral cavity & Anus | The mouth is formed by gut beingness tunneled into embryo. | The gut is tunneled into embryo and forms anus. |
| Archenteron | Have archenteron evolution in the early on stages of embryo formation. | In that location is no archenteron development. |
| Nature | They are always enteroceolus. | They tin be priapulids. |
| Nervous System | The nervous organisation is composed of hollow nervus cord and pharyngeal gill slits. | The nervous arrangement is solid, ventral nerve string. |
| Evolution | They are more evolved and complex in their body compositions. | They are less evolved and simple in their body compositions. |
| Cell Ciliation | They are all mono-ciliated. | They are multi-ciliated cells. |
| Division | They mainly include echinoderms, hemichordes and chordates | All the remaining bilaterian phyla are grouped into protostomes or are divided into two groups: protostomes and lophophorate. |
| Number Of Phyla | Deuterostomes contains less phyla and species than protostomes. | |
| Anus & Mouth Evolution | The mouth arises secondarily. | The anus arises secondarily. |
| Cleavage | Exhibit indeterminate cleavage. | Exhibit determinate cleavage. |
| Cleavage Shape | Undergoes radial cleavage. | Undergoes spiral cleavage. |
| Examples | Chordates, Echinoderms Pogonophora, Hemichordates and other college and complex organisms. | Flat worms, Annelids, Arthropods, Mollusks and other less complex organisms. |
Also Read: Difference Between Chordates And Not-Chordates
Source: https://vivadifferences.com/difference-between-protostomes-and-deuterostomes-with-examples/
Posted by: johnsonyoustion.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are The Major Differences Between Nervous Systems In Animal Phyla?"
Post a Comment